

Next: Orbital Angular Momentum
Up: White-Dwarf Stars
Previous: White-Dwarf Stars
- Consider a particle of mass
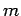 moving in a three-dimensional
isotropic harmonic oscillator potential of force constant
moving in a three-dimensional
isotropic harmonic oscillator potential of force constant 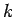 . Solve the
problem via the separation of variables, and obtain an expression for
the allowed values of the total energy of the system (in a stationary state).
. Solve the
problem via the separation of variables, and obtain an expression for
the allowed values of the total energy of the system (in a stationary state).
- Repeat the calculation of the Fermi energy of a gas of fermions by
assuming that the fermions are massless, so that the energy-momentum relation
is
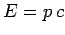 .
.
- Calculate the density of states of an electron gas in a cubic
box of volume
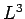 , bearing in mind that there are two electrons
per energy state. In other words, calculate the number of electron
states in the interval
, bearing in mind that there are two electrons
per energy state. In other words, calculate the number of electron
states in the interval 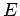 to
to 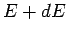 . This number can be written
. This number can be written
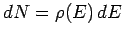 ,
where
,
where 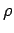 is the density of states.
is the density of states.
- Repeat the above calculation for a two-dimensional electron
gas in a square box of area
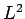 .
.
- Given that the number density of free electrons in copper is
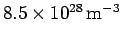 , calculate the Fermi
energy in electron volts, and the velocity of an electron whose kinetic
energy is equal to the Fermi energy.
, calculate the Fermi
energy in electron volts, and the velocity of an electron whose kinetic
energy is equal to the Fermi energy.
- Obtain an expression for the Fermi energy (in eV) of an electron in a white
dwarf star as a function of the stellar mass (in solar masses). At what
mass does the Fermi energy equal the rest mass energy?


Next: Orbital Angular Momentum
Up: White-Dwarf Stars
Previous: White-Dwarf Stars
Richard Fitzpatrick
2010-07-20